At its core, green building design is about planning and building structures which use less energy and resources to build and operate over the building’s lifespan than conventional buildings. Solar architecture can play a major role in the amount of energy required for heating, electricity, and domestic hot water.
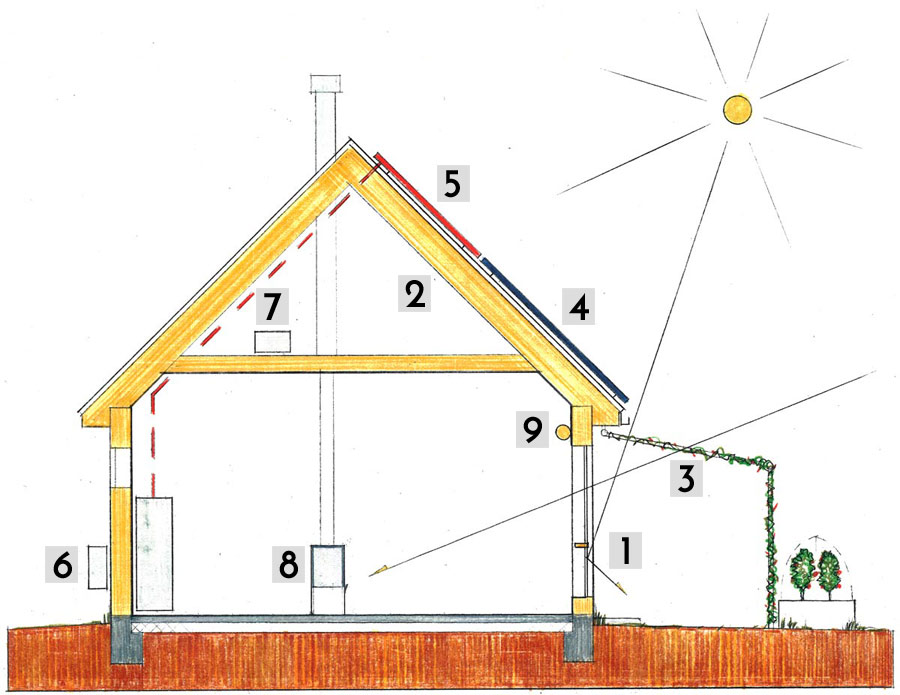
Features of the Passive Solar Home
- South wall windows – passive solar gain
- Insulated Envelope
- Shading – eave, awning or trellis
- Solar electric array
- Solar hot water system
- Heat pump – air to air
- Energy recovery ventilation (ERV)
- Wood stove
- Insulated curtains
Design Factors to Consider
Land Use
- Low impact site design & land use planning
- Determine solar building site
- Solar orientation & sun path
- 4 season landscape / food gardens
Building
- Creating a ‘healthy’ home
- Cold climate / building sciences
- High performance envelope
- Energy efficient construction
Solar
- Passive solar / direct gain
- Solar electric
- Solar thermal / hot water
Air
- 4 season air quality / passive cooling
- Ventilation/ ERV
- Low V.O.C. environment
Energy
- Minimize energy use
- Solar / renewable systems
- Clean energy technology
- Lower carbon emissions
- Eliminate direct petroleum use
Water
- Water cycle /well water
- Reduce demand/ efficiency
- Rainwater recovery
- Greywater separation
- Low impact landscape
Waste
- Reduce overall consumption
- Recycling
- Food /waste composting
- Composting toilet
Home Ecology
- Reduce consumption / less waste
- Resource conservation
- Solar energy / sunlight
- Trash / recycling
- Local food / farms
- Bio-fuel / wood
- Lower co2 emissions
- Composting toilet
Food Cycle
- Growing food / gardens
- Organic food / permaculture
- Food storage / harvest
- Pantry / root cellar
- Food waste/ composting
- Greenhouse
- Rainwater recovery
- Chickens / eggs